计算机的基础部件
The Basic Components of Computers
1 .The System Unit
The system unit is the core of your computer. It's inside the system unit that data is processed and stored.
The heart of the system unit is the CPU.The fact that your computer can run DOS means that the CPU in your computer belongs to the 8086 family of processors.This family includes the original 8086 as well as the 8088,the 80186,the 80286, the 80386,and the80486.
Although each of these processors has different capabilities, they can all run DOS.The CPU is the part of your computer that actually does the computing. Although the CPU performs manipulations on data. It can only hold data that it is currently working on. Most of the information in a computer is stored in the computer's main memory until TheCPU needs it. Memory is often called RAM, an acronym for Random Aclearcase/" target="_blank" >ccess Memory.
Basically, two things are stored in RAM:data and programs.When a program is executing, it re-sides in RAM, along with the data needed by the pro-gram.
2. Keyboards and Mouse
The basic input device on most microcomputer systems is a keyboard. Through the keyboard you “talk" to a computer. That is, it allows you to input information, instructions,or data to the computer.
Keyboards vary considerably from system to system, but most look a lot like a standard typewriter keyboard. Many also have a numeric keypad on the Right, which looks like the keypad on a 10-key adding machine. The keypad makes it easy to input large amounts of numerical data into the computer.
Computer keyboards usually have a number off unction keys.When pressed, a function key causes a particular action in the computer. For example, one key may tell the computer to clear the video screen of any information displayed, and another may tell the computer to send the information displayed on the screen to the printer so that a permanent copy can be obtained. Function keys are handy and convenient, since they allow you to “tell” the computer to do something by simply pressing one key!Keyboards without function keys often require you to press several keys in succession in order to give the computer one instruction.
Another common device is the mouse.You operate the mouse by moving it around the surface of your desk. As you move it, a special cursor called the mouse pointer moves around the screen in the same direction as you move the mouse. Programs that sup-port a mouse use the buttons on the mouse to select various options.
3 .Monitor
Video displays vary considerably in style and options.Some display in black and white;Others are amore eye pleasing green; and some can display in color. Many can display only standard upper and lower case letter, numbers and punctuation marks on the screen.
Better display can show text material in several intensities.For example, you may see a frequently used business form with the printed material appearing on the screen in a light or half intensity, while the instructions on how to fill it out are in bold or double intensity, and the information you type in may appear on the screen in standard intensity. Displays vary in terms of capacity as well.Some are able to display no more than 12 lines at once, with30 or 40 characters in each line. Most computers can show 24 or 25 lines with up to 80 characters in each. Like most things in life, the displays with more features generally cost more.
4. Floppy Disk and Fix Disk
There are two basic “flavors” of floppy drives:The 5.25-inch mini floppy and the 3.5-inch microfloppy.
As you can see in the Figure 1-4, both types of floppy disks have a write-protect notch. For the 5.25 inch floppy,when the write -protect notch is uncovered. The disk drive write data to the disk. When the notch is covered (using an adhesive strip usually sup-plied with the diskette), the drive can read from the disk but not write to it: for the 3.5 inch floppies, the mechanics are reversed. When the write-protect notch of a 3.5 inch diskette is covered,the disk can be writ-ten to. When the notch is uncovered,the disk cannot be written to. Unlike the mini floppy, to write-protect a microfloppy, you simply move a built in slider; no adhesive strip is required. In either case, when a disk cannot be written to, it is write-protected.
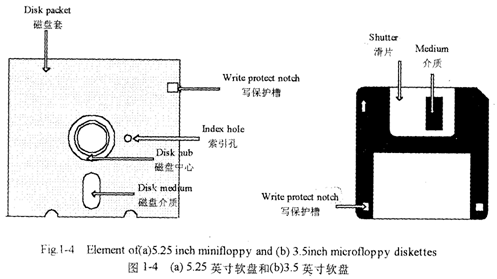
The magnetic medium that actually holds the information should be considered quite fragile. In the case of a minifloppy, a small portion of the medium is always exposed because the read-Native opening is uncovered. In the case of a microfloppy, the shutter protects the medium when the diskette is not in use. When a microfloppy is inserted into the disk drive, the shutter is opened automatically when the diskette is accessed. Because the magnetic medium is fragile and susceptible to contamination by dust or smoke and erasure by magnetic fields, above all else, remember this basic rule about diskettes:If the medium is dam-aged, it will be impossible to retrieve any information stored on that diskette.
Most likely, your computer contains at least one fixed disk. Fixed disks are also referred to as hard disks because their magnetic medium is rigid. As stated, the magnetic medium of a fixed disk is not removable. Your computer probably contains a fixed disk for two reasons:it is much faster at reading and writing information than a floppy drive and it can hold far more information. Fixed disks can hold any wherefrom 10 million to 1000 million bytes of information. In computers, the prefix mega (sometimes abbreviated) denotes 1 million. Therefore, if someone says that you have a 80 megabyte drive, this means it can hold about 80 million bytes of information.
One thing to remember about the fixed disk is that it is the most fragile component in your system. A severe shock can damage it. Therefore, make sure your system is located in a place that is free from excessive vibration.
5. Printer
Most microcomputer printers print one character at a time, usually at rates varying from 30 to perhaps180 characters per second. A more reasonable approach is to use a line printer, which, as the name implies, prints line by line instead of character by character. Rates of 1000 lines per minute (and more) are common. Even greater speed can be obtained by using a page printer to churn out complete pages at a time.
翻译:
计算机的基本部件
1.系统部件
系统部件是你计算机的核心。数据正是在系统部件内被处理和存储的。
系统部件的核心是CPU.你的计算机能运行DOS这个事实表明你的计算机中的CPU属于8086处理机系统。这个系统包括最早的8086和8088,80186,80286,80386和804860尽管这些处理机各有不同的能力,它们却能运行DOS. CPU正是你的计算机中实际进行计算的音区件。
虽然CPU能对数据进行操作,但是它只能保存当前正在处理的数据。大多数计算机中的信息存储在计算机的内存中,直到CPU需要使用它们。存储器也常称为RAM是随机存取存储器的缩略词。
基本上,在RAM中存储了两样东西:程序和数据。当一个程序执行时,它驻留在RAM中连同这个程序所需要的数据一道。
2.键盘与鼠标
大多数微型计算机的输入设备是键盘。你是通过键盘与计算机“对话”的。也就是说:它允许你将信息、指令或数据输入计算机。
计算机系统不同,键盘也会很不相同。但大多数键盘的外型与标准打字机键盘相似。许多键盘的右边还有一套数值键,它们看起来就像10键加法器上的小键盘。这种数值键使计算机可方便地进行大量数据录入。
计算机键盘上通常还有一些功能键。当按下功能键时,可在计算机上产生一个特殊的操作。例如, 一个键可以告诉计算机清除当前显示在屏幕上的任何信息,另一个键也许是告诉计算机将显示在屏幕上的信息打印出来功能键是非常方便的,因为通过它们简单地按一个键,便能让计算机完成相应工作。假如没有功能键.通常需要你同时连续地按几个键万能给计算机发出一条指令。
另一种普通类型设备是鼠标你把鼠标放在桌面上移动便可操纵它。你在移动它时,一个叫做鼠标指针的特殊光标沿着你移动鼠标的方向在屏幕上移动。支持鼠标的程序使用了鼠标上的按键来做各种选择。
3.显示器
显示器在式样、性能和配置上有许多种规格。有些显示器是黑白的;有些是使眼睛起来较舒服(不易疲劳)的绿色:有些能够显示彩色。多数显示器只能显示标准的大小写字母、数字和标点符号。
好的显示器能显示好几种亮度的文本。例如,你可以看到常用商业报表的表格线是以浅色或半亮度的色调显示在屏幕上,而表格中的文字信息则是以粗的或倍亮度的色调显示在屏幕上,你所键入的字符也许是以标准色调显示在屏幕上。
显示器在性能上有所不同。有些显示器只能显示12行,每行30至40个字符。大多数计算机能够显示24或25行,每行达80个字符。正如日常生活中的大多数事情一样,显示器性能愈好,其价格也就愈贵。
4.软盘与硬盘
有两种基本格调的软驱:使用5.25英寸的小型软盘驱动器和3.5英寸的微型软盘驱动器。
正如你在图1-4中所见,两种类型的软盘都有一个写保护槽。对5.25英寸软盘来说,当写保护槽是打开的时候,磁盘驱动器能向磁盘上写数据。当槽口被遮住时(常用随磁盘提供的不于胶软条),驱动器可从磁盘上读取信息但不能写信息到磁盘上;而对3.5英寸的软盘情况则相反,当3.5英寸软盘的写保护槽被遮住时,能向磁盘上写信息,当槽口敞开时,则不能往盘上写信息。不像小型软盘那样,为微软盘加写保护,只需移动盘内固有的滑片即可,不需要使用不干胶软条。无论在哪种情况下,当不能往磁盘上写信息时,磁盘处写保护状态。
应该知道,实际存储信息!性媒体是很易被损坏的。就小盘而言,因为读写孔是敞开的以媒体的一小部分总是暴露在就微软盘而言,当软盘不用时,遮板保护着媒体。把一片微软盘插进磁盘驱动器中,当对磁盘进行访问时,遮板自动地被打开。由于磁性媒体是易受损的,而且对灰尘或烟雾的污染和对磁场的消除信息极为敏感最重要的是,记住这个关于磁盘的基本原则:如果媒体受到损害,就不可能检索出存储在磁盘上的任何信息了。
多数情况下,计算机至少含有一个硬盘固定盘也被称为硬盘,因为它们的磁性媒体是硬性的。正如所述的,硬盘的磁性媒体是不可移动的飞你的计算机可能含有一个硬盘是基于这两个原因:它读写信息的速度远比软盘快得多,而且它能存储多得多的信息。硬盘在任何地方都可存储10兆到1000兆字节的信息在计算机领域,前缀mega(有时缩写为M)表示1兆。所以,如果说你有80兆字节的驱动器,这意味着它能存储约80兆字节信息。
关于硬盘应记住的一件事是:它是你的系统中最脆弱的部件,剧烈的震动就会损坏它。所以,要确保你的系统被放置在一个无过分振动的地方。
5.打印机
大多数微型机上的打印机一次打印一个字符,其打印速度大致在每秒30至180个字符之间。比较合理的方案是采用行式打印机输出。顾名思义,所谓行式打印机就是一行一行的,而不是一个字符一个字符地打印输出。它们通常的打印速度是每分钟1000行以上;若使用每次打印输出一页的页式打印机我们还可以获得更快的打印速度。





